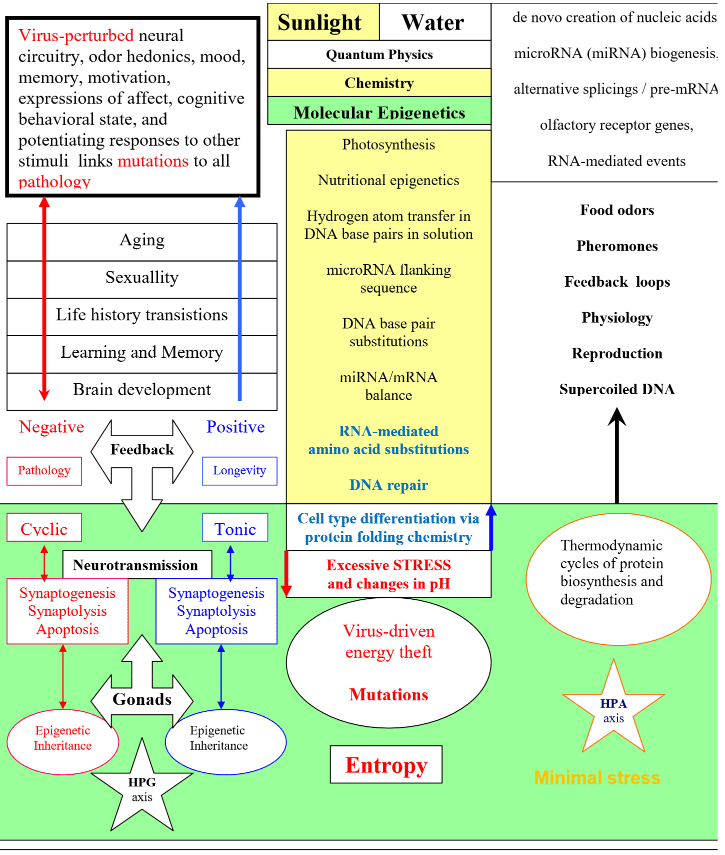
microRNA-mediated quantum error correction (4)

I’ve posted presentation abstract submissions here because I anticipated they would not be selected for presentation. See: UV light, H2O, and epigenetic effects… (1) 9/25/20 Submitted by James V. Kohl on 9/25/20 for presentation during the Epigenetics – From Bench to Clinic session: RNA modifications and epitranscriptomics Moderator Tony Kouzarides Conclusion: Theorists who ignore the … microRNA-mediated quantum error correction (4)