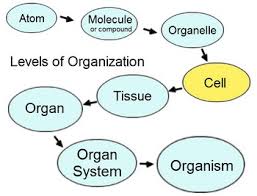
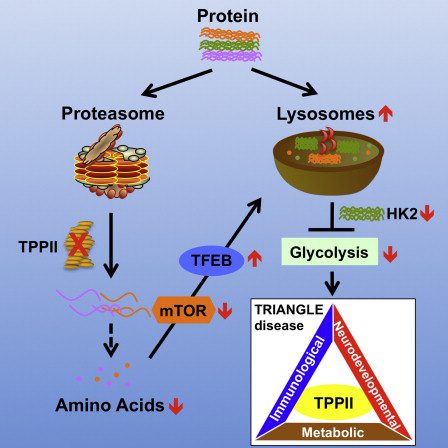
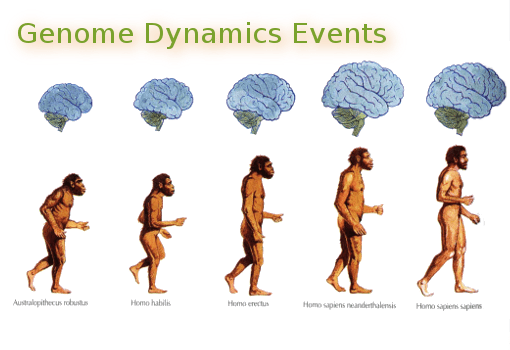
Polycombic ecological adaptation as a science, not a theory
Multi-omic data integration enables discovery of hidden biological regularities Excerpt: Tracing the central dogma of biology (left column), we can link specific data types (middle column) to explain each of these biological processes. In this work, novel biological regularities that relate these processes are discovered through: (i) primary omics data (top box, right column) … Polycombic ecological adaptation as a science, not a theory