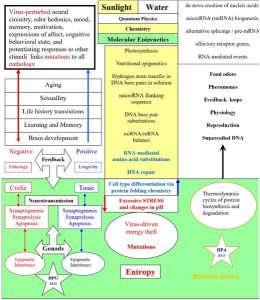
WHO broke the breakthough (9)
(click to enlarge)
Optimal Nutritional Status for a Well-Functioning Immune System Is an Important Factor to Protect against Viral Infections (4/23/20) Facts about RNA-peptide interactions at the origin of life and the origin of consciousness were linked to moronic theories in the current issue of Science Magazine.
See: Zoonomia 4/27/23
Search for the articles included: zoonomia consortium to read how much pseudoscientific nonsense is linked to the energy-dependent biophysically constrained Creation of new species.
See:
Relating enhancer genetic variation across mammals to complex phenotypes using machine learning
“Protein-coding differences between species often fail to explain phenotypic diversity…”
Protein folding chemistry is epigenetically effected and biophysically constrained by the physiology of reproduction across kingdoms.
Leveraging base-pair mammalian constraint to understand genetic variation and human disease
“…the regulatory landscape of the human genome still needs to be further explored and linked to disease.”
The virus-driven degradation of messenger RNA (mRNA) has been linked to all diseases since the origin of life and origin of consciousness.
Three-dimensional genome rewiring in loci with human accelerated regions
“…comparative genomics together with models of 3D genome folding revealed enhancer hijacking as an explanation for the rapid evolution of HARs.”
Light activated carbon fixation in cyanobacteria biophysically constrains pH-dependent miRNA-mediated reproduction. Use of the term “enhancer hijacking” obfuscates every aspect of top-down quantum causation, physics, chemistry, and molecular epigenetics.
Integrating gene annotation with orthology inference at scale
‘TOGA implements a different paradigm to infer orthologous loci, improves ortholog detection and annotation of conserved genes compared with state-of-the-art methods, and handles even highly fragmented assemblies.”
Inferences were eliminated by facts that link natural selection for energy-dependent codon optimality to Darwin’s “conditions of life” via the physiology of reproduction.
Evolutionary constraint and innovation across hundreds of placental mammals
Of 101 million significantly constrained single bases, 80% are outside protein-coding exons and half have no functional annotations in the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE) resource.
The energy-dependent changes in genes and regulatory elements link fixation of amino acid substitutions to exceptional mammalian traits via the physiology of reproduction in bacteria, which links mutations to imperiled biodiversity in the context of 6515 genetic variants that have been linked to the origin of life ~6000 years ago via analysis of 6,515 exomes, genome function and organismal phenotypes.
The functional and evolutionary impacts of human-specific deletions in conserved elements
“We identified and characterized 10,032 human-specific conserved deletions (hCONDELs). These short (average 2.56 base pairs) deletions are enriched for human brain functions across genetic, epigenomic, and transcriptomic datasets.’
Their data provide no facts that might otherwise be linked to the evolutionary mechanisms that they claim drive new traits in humans and other species.
Comparative genomics of Balto, a famous historic dog, captures lost diversity of 1920s sled dogs
“We propose that Balto’s population of origin, which was less inbred and genetically healthier than that of modern breeds, was adapted to the extreme environment of 1920s Alaska.”
If the population of origin fails to adapt, the species becomes extinct.
A genomic timescale for placental mammal evolution
“We compared neutral genome-wide phylogenomic signals using concatenation and coalescent-based approaches, interrogated phylogenetic variation across chromosomes, and analyzed extensive catalogs of structural variants.”
Food energy-dependent pheromone-controlled chromosomal rearrangement in species from flies to humans link ecological adaptation to all biodiversity.
Mammalian evolution of human cis-regulatory elements and transcription factor binding sites
“Genes near constrained elements perform fundamental cellular processes, whereas genes near primate-specific elements are involved in environmental interaction, including odor perception and immune response.”
Odor perception and the immune response link food odors and pheromones to biophysically constrained viral latency via RNA interference (RNAi) across kingdoms.
The contribution of historical processes to contemporary extinction risk in placental mammals
“Models that included genomic data were predictive of species’ conservation status, suggesting that, in the absence of adequate census or ecological data, genomic information may provide an initial risk assessment.”
Models that fail to link ecological data to species’ conservation status cannot be validated. They are missing key elements of the links from top-down quantum causation to coherently organized biology via the Creation of miRNAs in exosomes.
Insights into mammalian TE diversity through the curation of 248 genome assemblies
“Mammals tend to accumulate only a few types of TEs at any given time, with one TE type dominating. We also found association between dietary habit and the presence of DNA transposon invasions.”
Pardis Sabeti’s group linked a single base pair change, from EDAR V370A polymorphisms to differences in morphological and behavioral phenotypes across human populations in 2013.
Want more on the same topic?
Swipe/Drag Left and Right To Browse Related Posts:
Energy-as-information & the aurora borealis (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Energy-as-information & the aurora borealis (1)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (10)
3 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (9)
3 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (7)
2 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (4)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Pea protein, p53 and cancer prevention (1)
2 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (10)
< 1 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (7)
< 1 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (6)
2 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (5)
5 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (4)
2 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (3)
4 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (2)
2 MIN READ
0
The bioweapons cartel (1)
4 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (9)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (8)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (7)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (4)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Whistleblowers found: dead or alive (1)
3 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (10)
5 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (7)
3 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (6)
2 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (5)
3 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (4)
< 1 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (3)
< 1 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (2)
3 MIN READ
0
NGS vs 5th generation warfare (1)
3 MIN READ
0
Not necessary. Not safe. Not effective (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Not necessary. Not safe. Not effective (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Not necessary. Not safe. Not effective (7)
2 MIN READ
0
Not necessary. Not safe. Not effective (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Not necessary. Not safe. Not effective (1)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (10)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (9)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (8)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated preditions (7)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (6)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (5)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (4)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (3)
< 1 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated predictions (2)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated preditions (1)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (10)
5 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (8)
4 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (7)
2 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Minimal level of conflict (1)
4 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (10)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (9)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (8)
2 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (7)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (5)
4 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Biorealism (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (9)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (8)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (7)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (4)
3 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (2)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Total recall 6000 years (1)
3 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (10)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (9)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (8)
2 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (5)
3 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (4)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Censorship of perception (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Biochemical is geopolitical (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (9)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (8)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (7)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (4)
3 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Biogeochemical is geopolitical (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (10)
4 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (9)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (7)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (4)
4 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Flipping off the flipons (2)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (9)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (8)
7 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (7)
3 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (6)
4 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (5)
3 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Patenting the sun (1)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (10)
2 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (9)
2 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (6)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (4)
3 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Positive as a proton (1)
2 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (10)
3 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (7)
< 1 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (6)
2 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (3)
6 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (2)
2 MIN READ
0
WHO broke the breakthrough (1)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated epigenetic effects (10)
3 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated epigenetic effects (9)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated epigenetic effects (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated epigenetic effects (6)
2 MIN READ
0
miRNA-mediated epigenetic effects (5)
6 MIN READ
0
The devil is in the dirt (3)
5 MIN READ
0
The devil is in the dirt (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Scientism, Atheism and Theology (9)
2 MIN READ
0
Scientism, Atheism & Theology (6)
2 MIN READ
0
Scientism, Atheism & Theology (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Pheromone-regulated genetic processes (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Photonics in Forensics (8)
4 MIN READ
0
microRNA-mediated biodiversity (2)
2 MIN READ
0
microRNA-mediated biodiversity (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent ‘futile cycles’ of autophagy
2 MIN READ
0
From quantum physics to quantum souls (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Sympatric Speciation vs pseudosceintific nonsense (4)
2 MIN READ
0
Polymaths and paradigm shifts: from Asimov to Bear (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Ecological adaptation: A new definition of heredity (3)
4 MIN READ
0
Subatomic: From thermophiles to humans (2)
6 MIN READ
0
Enzyme-constrained interethnic diversity (8)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Enzyme-constrained interethnic diversity (7)
6 MIN READ
0
A Mathematical Model Links Quantum Physics to Quantum Souls (1)
6 MIN READ
0
Kinetically Stable Thermodynamically Activated Cell Metabolism (1)
3 MIN READ
0
Agilent technology and energy-dependent autophagy
8 MIN READ
0
The overwhelming ignorance of sex researchers
5 MIN READ
0
Mouse morphs and primate diversity in 50 years
7 MIN READ
0
Light-activated error free DNA repair (2)
8 MIN READ
0
MicroRNAs and the Cassandra syndrome (revisited)
4 MIN READ
0
Pheromones biophysically constrain RNA-mediated biodiversity (1)
5 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent structure and function: Until death (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent structure and function: Until death (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent structure and function: Until death (1)
4 MIN READ
0
Host-derived creation of all pathology (1 of 2)
5 MIN READ
0
Your indifference is killing you and others (4)
4 MIN READ
0
Robert Sapolsky’s legacy of atheistic pseudoscientific nonsense
4 MIN READ
0
Can protein folding chemistry be understood by theorists?
5 MIN READ
0
Irreconcilable differences: food energy vs de novo assembly
2 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent physical and biophysical constraints (6)
8 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent physical and biophysical constraints (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Cell type assembly and the space-time continuum
2 MIN READ
0
God’s shrinking role in salvation (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Draining the academic swamp of parasites
3 MIN READ
0
Viruses in pathogenic variants disrupt alternative splicings (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Respiration-dependent endogenous RNA interference
4 MIN READ
0
Cytosis: Biology Content
7 MIN READ
0
Harvard researchers support young earth creationism
< 1 MIN READ
0
Thinking about energy is not radical re-thinking
6 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent pheromone-controlled entropy (2)
6 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent allelic imbalances, viruses, and pathology
3 MIN READ
0
Biologically uninformed biologists fight back and lose
3 MIN READ
0
Stuart Kauffman refutes theistic evolution
3 MIN READ
0
May the anti-entropic force of sunlight be with you
4 MIN READ
0
Happy Darwin Day (2017)
4 MIN READ
0
Physicists: Desperate Acts (revisited)
6 MIN READ
0
Dobzhansky 1973 and precision medicine (4)
5 MIN READ
0
Science journalists or paid propagandists? (4)
6 MIN READ
0
Dobzhansky 1973 and precision medicine
6 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent alternative splicings 1996 – 2016 (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Anti-entropic virucidal energy as information
10 MIN READ
0
Explorers who do not know what is known (2)
6 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent de novo creation and neurogenesis
7 MIN READ
0
Light, behavior and autophagy, a gender-specific risk factor
4 MIN READ
0
Controlled amino acid treatment of all pathology
4 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated “repurposing” is autophagy
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated "repurposing" is autophagy
2 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics and autophagy vs mutations and evolution (8)
4 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent maternal-to-zygotic transition
6 MIN READ
1
Epigenetically effected energy-dependent fluorescence
5 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics and autophagy vs mutations and evolution (7)
3 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics and autophagy vs mutations and evolution (5)
2 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics and autophagy vs mutations and evolution
< 1 MIN READ
0
From Precis to Proof in 6000 years (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Coulombic interactions facilitate polycombic adaptation
5 MIN READ
0
Top-down adaptation vs bottom-up evolution
6 MIN READ
0
Light ‘drives’ adaptation; nothing ‘drives’ evolution (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Did evolution autophosphorylate your kinases? (3)
2 MIN READ
1
Virus-mediated hecatombic evolution
2 MIN READ
0
Hecatombic evolution via oncocers and oncohistones
9 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent autophagy
3 MIN READ
0
Life is energy-dependent task management
3 MIN READ
0
Hypothesis free pseudoscience vs facts (1)
5 MIN READ
0
Hydrogen-atom energy in DNA base pairs
6 MIN READ
0
Light energy-dependent active motifs
6 MIN READ
0
DNA repair via junk DNA (1)
5 MIN READ
0
Conserved biophotonic emissions
7 MIN READ
2
The Origin of Information (2)
6 MIN READ
0
Did “Nature” kill Steve Jobs? (3)
10 MIN READ
0
Funding the Human Genome Project-Write
2 MIN READ
0
MicroRNAs and sexual orientation
8 MIN READ
0
RNA methylation, learning, memory and behavior,
< 1 MIN READ
0
Major transition ends use of silly theories
5 MIN READ
0
RNA methylation
2 MIN READ
0
War Games: False Flag Terrorism
5 MIN READ
0
Magic, Miracle, or Molecular Mechanism (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent creation and entropy
4 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated physics, chemistry, and molecular epigenetics (4)
5 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated physics, chemistry, and molecular epigenetics (3)
5 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated physics, chemistry, and molecular epigenetics
9 MIN READ
0
Wasted Templeton Funding (4)
3 MIN READ
0
RNA splicing, genetic variation, and disease
2 MIN READ
0
Ricki Lewis’ Time Machine (3)
5 MIN READ
0
Creating nutrient-dependent life with enough genes to survive
3 MIN READ
0
Confusing effects and affects of visual input
2 MIN READ
0
Energy-dependent purpose vs teleophobic telorexia
12 MIN READ
0
Stress-linked population-level history dependence
5 MIN READ
0
Do not miss the misrepresentations
2 MIN READ
0
Energy dependent RNA-mediated immunity (5)
4 MIN READ
0
Energy dependent RNA-mediated immunity (4)
6 MIN READ
0
Energy dependent RNA-mediated immunity (3)
8 MIN READ
0
Energy dependent RNA-mediated immunity (2)
10 MIN READ
0
The toxic river of neo-Darwinian pseudoscience
3 MIN READ
0
Science vs semantics
4 MIN READ
0
From angstroms to ecosystems and entropy
2 MIN READ
0
Bacteria see the light and they adapt (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Soil bacteria, bulls, cows, microRNAs, and mammary glands (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Soil bacteria, bulls, cows, microRNAs, and mammary glands
3 MIN READ
0
Bringing RNA back to epigenetics (20 years later)
11 MIN READ
0
Effects on invertebrate GnRH and affects on primate behavior
6 MIN READ
0
Creating gravity, nucleic acids, receptors, and supercoiled DNA (2)
9 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent RNA-mediated cause and effect
3 MIN READ
0
Creating gravity, nucleic acids, receptors, and supercoiled DNA
2 MIN READ
0
Bacteria see the light and they adapt
7 MIN READ
0
Models of scientific literacy
3 MIN READ
0
Organic Compounds and the Miracle of Smell and Taste
7 MIN READ
0
Cancer: Evolution 2.0’s Blind Spot
13 MIN READ
0
Despicable fools?
4 MIN READ
0
Ricki Lewis’ Time Machine
5 MIN READ
0
Virus-perturbed alternative splicings
3 MIN READ
0
Brain evolution?
< 1 MIN READ
0
Center stage RNA-mediated events (since 1996)
3 MIN READ
0
Blood test links atoms to ecosystems
2 MIN READ
0
A failed theory of cancer: two more decades of pseudoscience
5 MIN READ
0
Genes, orchid odors, and pheromones from blonds
5 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated theory killers (11) (12) (13) (14) (15)
7 MIN READ
0
Finding peace and π in the light of H bond energy (2)
8 MIN READ
0
MicroRNA-mediated RNA epigenetics
2 MIN READ
0
RNA methylation, RNA-directed DNA methylation, learning and memory
3 MIN READ
0
Finding peace and π in the light of H bond energy
5 MIN READ
0
Assumptions prove ignorance
5 MIN READ
0
Neo-Darwinian sink testing
2 MIN READ
0
Life history transitions and RNA-mediated survial
2 MIN READ
0
Did Brain Atrophy Evolve?
2 MIN READ
0
Did Dobzhansky see the UV light of creation?
10 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated theory killers (6) (7) (8) (9) (10)
5 MIN READ
0
Does metabolism link beneficial mutations to cancer?
10 MIN READ
0
Hydrogen-Atom Transfer in DNA Base Pairs (3)
3 MIN READ
0
Manufacturing fossil “evidence”
4 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated theory killers (3)
7 MIN READ
0
Essential pseudoscientific concepts of atheism
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated theory killers (2)
8 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated theory killers
6 MIN READ
0
Natural cooperation and Evolution 2.0
6 MIN READ
0
A million dollar paradox?
2 MIN READ
0
A two-faced protein enables RNA-mediated DNA repair (4)
6 MIN READ
0
A two-faced protein enables RNA-mediated DNA repair (5)
4 MIN READ
0
A two-faced protein enables RNA-mediated DNA repair (3)
8 MIN READ
0
Teaching the biologically uninformed
3 MIN READ
0
Innovative Neurotechnologies Link Sunlight to Precision Medicine
4 MIN READ
0
Hydrogen-Atom Transfer in DNA Base Pairs
9 MIN READ
0
Neo-Darwinism vs the neocortex
4 MIN READ
0
A two-faced protein enables RNA-mediated DNA repair
2 MIN READ
0
Plasma created by sunlight and RNA–mediated epigenetic heredity
2 MIN READ
0
Positive feedback loops and epigenetic traps
2 MIN READ
0
Behavioral Immune System model
4 MIN READ
0
Stress-perturbed mitochondrial dysfunction
4 MIN READ
0
Understanding cell type differentiation
3 MIN READ
0
Let there be anti-entropic light (3)
6 MIN READ
0
Theorists can’t understand biology
6 MIN READ
0
Neuroplasticity
4 MIN READ
0
Sensationalizing no new mechanism
2 MIN READ
0
Cell type differentiation: atoms to ecosystems
2 MIN READ
0
Too complex for the Complex Biological Systems Alliance
4 MIN READ
0
Rediscovering quantum behavior
2 MIN READ
0
From dust to genomic entropy?
3 MIN READ
0
Virus, transposon and plasmid evolution
< 1 MIN READ
0
Models are not theories (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Models are not theories (1)
2 MIN READ
0
Fossils vs cell types and the brain
3 MIN READ
0
Can veterans and other prisoners escape pseudoscience?
2 MIN READ
0
eQTLs and ecological adaptation
< 1 MIN READ
0
RNA central and RNA-mediated.com
6 MIN READ
0
Ecological speciation. Get it, theorists?
< 1 MIN READ
0
Designing, engineering, and protecting biodiversity
3 MIN READ
0
The virome, microbiome, replisome and supercoiled DNA
2 MIN READ
0
Skip the politics; embrace the facts
5 MIN READ
0
Controled Stem Cell Expansion
3 MIN READ
0
Neo-Darwinian logic is nonsense
3 MIN READ
0
FREE* SAMPLE: Histone modification
4 MIN READ
0
700 million years of evolution?
5 MIN READ
0
Biophysically constrained or unconstrained?
2 MIN READ
0
Mutated mitochondrial genes vs Supercoiled DNA
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated retrotransposon-mediated biodiversity
3 MIN READ
0
Mystery machine vs model (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Mystery machine vs model
2 MIN READ
0
Mystery machine vs medical intelligence
2 MIN READ
0
The Current State of Neuroscience
3 MIN READ
0
Cancer: forward and reverse
2 MIN READ
0
Energy and evolution: another opinion?
2 MIN READ
0
Bird watchers and RNAs in cancers
2 MIN READ
0
Supercoiled DNA constrains virus-driven genomic entropy
2 MIN READ
0
Let there be anti-entropic light (2)
4 MIN READ
0
Foundamentals of theory
4 MIN READ
0
Microbes to humans 2015 Nobel Prize
2 MIN READ
0
Is mainstream science in “Science” pseudoscience?
5 MIN READ
0
Mechanisms of stress: from genes to cancer
9 MIN READ
0
Viruses come alive: Tree of life pseudoscience
6 MIN READ
0
Theorists have not seen the light (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Hijacked light energy and vertebrate pathology
4 MIN READ
0
Theorists have not seen the light
4 MIN READ
0
A 5-10K comparison of design principles to evolution
3 MIN READ
0
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing and ecological adaptation
7 MIN READ
0
Nucleic acids: Stability of DNA/RNA
2 MIN READ
0
Exosomes and the RNA-mediated future of medicine (3)
2 MIN READ
0
Exosomes and the RNA-mediated future of medicine (2)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Exosomes and the RNA-mediated future of medicine
5 MIN READ
0
Multi-omic analysis features (SNPs, miRNA)
3 MIN READ
0
Anti-entropic effects on the origin of life
< 1 MIN READ
0
Somatic hypermutation vs RNA-mediated events
2 MIN READ
0
From fertilization to RNA-mediated events and back
2 MIN READ
0
Phytochemical link from the sun to cell types
2 MIN READ
0
Metabolic competition and cancer
2 MIN READ
0
Natural selection: an anti-entropic force?
2 MIN READ
0
Genome sequencing, cadherins, and quantum consciousness
6 MIN READ
0
“New” quantum biology. Pirating the old
3 MIN READ
0
Creating genes and species
3 MIN READ
0
Cell types, SNVs, CNVs, and chromosomes
3 MIN READ
0
A “new” code enables ecological adaptation
4 MIN READ
0
Thermotolerance and Longevity
57 MIN READ
0
Is life the balance between quantum and classical physics?
3 MIN READ
0
Anti-entropic containment of energy: symbiosis 1.0
5 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated X chromosome inactivation
3 MIN READ
0
The “great filter” is an epigenetic trap
4 MIN READ
0
Atomic-resolution of cell type signaling
4 MIN READ
0
Unraveling evolutionary pseudoscience
2 MIN READ
0
Eibi Nevo gets it wrong
3 MIN READ
0
Rs3827760 is Val370Ala and EDARV370A
3 MIN READ
0
From “Blood Music” to Evolution 2.0
5 MIN READ
0
Olfaction & the octopus and human genomes
3 MIN READ
0
Protosuns, prebiotic molecules, proteins, and people
4 MIN READ
0
Mammalian-wide interspersed repeats (MIRs)
2 MIN READ
0
Ecological speciation vs revised evolutionary syntheses
6 MIN READ
0
Ecology replaces the extended evolutionary synthesis
4 MIN READ
0
The stability of organized genomes (4)
3 MIN READ
0
The stability of organized genomes (3)
3 MIN READ
0
The stability of organized genomes (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Epimutation.com: a domain of confusion
8 MIN READ
0
Light -induced nucleic acid-mediated gene duplication?
< 1 MIN READ
0
Is the best Chinese research from China?
3 MIN READ
0
The stability of organized genomes
5 MIN READ
0
Viruses, amino acids, and somatic cell types (3)
9 MIN READ
0
Viruses, amino acids, and somatic cell types (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Big Bang Cosmology vs Reality
< 1 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated terms of virus-induced en-deer-ment
2 MIN READ
0
Domestication via a single amino acid substitution
2 MIN READ
0
Hematopoiesis and practopoiesis
4 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated morphological AND behavioral phenotypes
2 MIN READ
0
Easy editing: Reinventing our RNA world
3 MIN READ
0
Is photic-zone ribosomal diversity linked to all biodiversity?
2 MIN READ
0
Picornaviruses moving between primates (or not)
2 MIN READ
0
Riding the wrong direction
3 MIN READ
0
Decreased phenotypic variation: Faith in Facts
7 MIN READ
1
Faithfully repaired DNA
5 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated gene duplication, fixation, and ecological adaptation
6 MIN READ
0
MicroRNA controlled growth and brain development
7 MIN READ
0
MicroRNA – controlled ecological adaptations
5 MIN READ
0
Celebrating independence from ridiculous theories
3 MIN READ
0
“New” epigenetic mechanism for lifelong learning?
3 MIN READ
0
The sum of our RNA-mediated parts
2 MIN READ
0
Protein folding and Google page rank
2 MIN READ
0
Iron, ferritin, thyroxine
2 MIN READ
0
“Evolution” of sex differences?
2 MIN READ
0
Nutrient stress-induced RNA-mediated pathology
< 1 MIN READ
0
Amino acid substitutions are not mutations
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated events from A to Z
2 MIN READ
0
What I cannot create I eliminate from discussion
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated development
2 MIN READ
0
Creating and maintaining the human virome
2 MIN READ
0
Healthy mutants
2 MIN READ
0
Uniquely epigenomic gene regulation
2 MIN READ
0
MicroRNAs and inappropriate functions
2 MIN READ
0
Rejecting pseudoscientific nonsense
6 MIN READ
1
Living the life that randomness created? (Sarcasm alert)
3 MIN READ
0
30 years of theoretical nonsense
3 MIN READ
0
microRNAs, glycosylation, and genomes
4 MIN READ
0
Unknown mechanisms and conclusions
2 MIN READ
0
Alternative splicings: epigenetics meets pharmacogenomics
4 MIN READ
0
Epigenetic regulation of aging by glycine and GnRH
5 MIN READ
0
Physicians who practice evolutionary medicine?
3 MIN READ
0
Pattern recognition: biogeochemical structure and function
5 MIN READ
0
Tweaking the story to fit the theory
5 MIN READ
0
Appetite for ingesting theories (raw)
< 1 MIN READ
0
I forgot. How do mutations cause evolution?
4 MIN READ
0
One amino acid substitution, genes, and brain activity
3 MIN READ
0
Batch effect vs epigenetic effects
3 MIN READ
0
Gene expression, immortality, and cancer
6 MIN READ
0
Missing a fact: microRNAs are genomic biomarkers
4 MIN READ
1
Bee-birthed epigenetics and primate cell types
5 MIN READ
0
A lighting requirement for life
11 MIN READ
3
Scientists lose. A sci-fi author gains credibility
2 MIN READ
0
Vitamin B3 and DNA repair
4 MIN READ
0
Bees and primates automagically evolve
3 MIN READ
0
Ignoring systems complexity (it’s too complicated)
3 MIN READ
0
Five years of Ferguson
2 MIN READ
0
Computing via phosphorylation and fixation
3 MIN READ
0
Virus-driven cancer treatment and prevention
2 MIN READ
0
The microbiome, pharmacogenetics, and privacy
< 1 MIN READ
0
Retinoic acid + one receptor regulate the genome
3 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics: microRNAs effect an integrative pathway
4 MIN READ
0
Protein isoforms do not evolve
3 MIN READ
0
Tissue type variation and expression of genes
< 1 MIN READ
0
From gut bacteria to breast milk and back
5 MIN READ
0
Chance mutations — not natural selection
5 MIN READ
0
Viruses in gut microbes
4 MIN READ
0
Physics, chemistry, light, and life
2 MIN READ
0
Finding odor and taste receptors everywhere
6 MIN READ
0
Linking the origin of birds to dinosaurs
< 1 MIN READ
0
An epigenetic mark links algae, worms, and flies
2 MIN READ
0
Effect and affect of a single base-pair change
4 MIN READ
0
Tet3 regulation of nutrient-dependent cell type differentiation
4 MIN READ
0
Thermodynamics and protein folding landscapes
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated silencing of a chromosome
3 MIN READ
0
Viruses, proteins, and gut metagenomes do not evolve
< 1 MIN READ
0
Pathology constrains X-linked evolution
2 MIN READ
0
Feedback loops link insects to human brains
2 MIN READ
0
Viruses and cell type differentiation
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated cell types and precision medicine
5 MIN READ
0
DNA Methylation and organized genomes (2)
10 MIN READ
0
DNA Methylation and organized genomes
7 MIN READ
0
Misunderstanding cancer
7 MIN READ
0
Amino acid-dependent cell type differentiation
8 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent RNA interference (2)
4 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent RNA interference
4 MIN READ
0
Mutisensory integration: watching the paradigm shift
12 MIN READ
0
Origin of life and cancer (1,2,3)
2 MIN READ
0
A genetic variant refutes neo-Darwinism
6 MIN READ
0
MicroRNAs and invasive phenotypes
< 1 MIN READ
0
Silencing genes and serious scientists
3 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent microRNAs control cell types
6 MIN READ
0
Deeply ingrained thoughts
< 1 MIN READ
0
Graphic misrepresentations of ecological adaptation
2 MIN READ
0
Too many targets for theories
3 MIN READ
0
Methylation maintains cell type differences (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Methylation maintains cell type differences
3 MIN READ
0
Creating nothing but a theory (3)
4 MIN READ
3
Creating nothing but a theory (2)
4 MIN READ
0
Creating nothing but a theory
4 MIN READ
0
Viruses and ecologically adapted animals
2 MIN READ
0
2 genes in 2 species (too expensive and too insignificant)
11 MIN READ
0
The quantum / classical RNA-mediated ‘tipping point’
3 MIN READ
0
Epigenetic effects of soil bacteria on plants
< 1 MIN READ
0
Epigenetic switch links MicroRNAs to RNA-protein interactions
4 MIN READ
0
Quantum correlations/pseudoscience
3 MIN READ
0
Anti-entropic solar energy
5 MIN READ
0
Mimicking claims and ignoring facts
4 MIN READ
0
Correctly modeling life on this planet
3 MIN READ
0
Correctly modeling ecological adaptation
4 MIN READ
0
Behavior (4): All responses are RNA-mediated in birds
4 MIN READ
0
Questions about life’s diversity
21 MIN READ
0
UV-light mutations and gene loss (not gain)
5 MIN READ
0
Virus-driven origin of life
2 MIN READ
0
Luis P. Villarreal tells it like it is
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-directed gene choice
5 MIN READ
0
Walk towards the light
< 1 MIN READ
0
Two types of microRNA are not double agents
2 MIN READ
0
Epigenetics Skeptism
5 MIN READ
0
Assembling yourself: Molecular self / other recognition
4 MIN READ
0
What about birds?
5 MIN READ
0
Virus-driven cell type differentiation
2 MIN READ
0
RNA directed DNA methylation and cell types
4 MIN READ
0
Implicating microRNAs in cancer
2 MIN READ
0
Rejecting what is known about viral microRNAs and nutrient-dependent microRNAs
2 MIN READ
0
Reverse phosphorylation
7 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated repurposing in microbes and adaptations in primate brains
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated “repurposing” is nutrient-dependent and pheromone-controlled
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated "repurposing" is nutrient-dependent and pheromone-controlled
3 MIN READ
0
From 3-D to epigenetically-effected 4-D genome make-up
5 MIN READ
0
Let there be anti-entropic light (1)
11 MIN READ
0
An epigenetic trap (the prequel)
5 MIN READ
0
Imagining that data historically supports evolutionary theory
7 MIN READ
0
Atheism: Arrogant, useless, and divisive ignorance
7 MIN READ
0
The anti-entropic force of "Nature"
2 MIN READ
0
Nutritional epigenetics, exercise, and immune system integrity
4 MIN READ
0
What if Darwin was not still dead?
2 MIN READ
0
Military combat training to fight disease (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Military combat training to fight disease
3 MIN READ
0
Theoretical physics and molecular biology
5 MIN READ
0
Atoms to ecosystems is not almost a molecular ecology
3 MIN READ
0
Epigenetic effects of viruses on cellular homeostasis (2)
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated epigenetic modification via DNA-methylation
4 MIN READ
0
Quantum physics, quantum biology, and quantum consciousness
4 MIN READ
0
How fast can evolutionary theory be changed?
5 MIN READ
0
Biological energy and a microbiome model of a light-driven time machine
3 MIN READ
0
The biologically-based origin of the mammalian placenta (2)
6 MIN READ
0
Quantum Superpositions: let there be light
4 MIN READ
0
Are viruses microRNAs? (2)
5 MIN READ
0
Are viruses microRNAs?
3 MIN READ
0
Sneaking up from behind (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Sneaking up from behind
4 MIN READ
0
Quantum entanglement, mass, and biomass
4 MIN READ
0
Physicists: Desperate Acts
16 MIN READ
0
An epigenetic trap (the sequel)
10 MIN READ
0
Mute points: most are afraid to mention them
6 MIN READ
0
All of “like kind” (Part 2)
2 MIN READ
0
All of "like kind" in the (bigger) family
6 MIN READ
1
Environment epigenetically shapes the immune system
3 MIN READ
0
Beneficial microbes kill beneficial mutations
4 MIN READ
0
Constrained evolution is ecological adaptation
5 MIN READ
0
A single amino acid substitution differentiates cell types of E. coli
3 MIN READ
0
Unconstrained evolutionary innovability
4 MIN READ
0
RNA-protein interactions reveal biophysical to ecological landscapes
2 MIN READ
0
Mutagenesis: Replacing facts with theories
5 MIN READ
0
ISHE's human ethology group
2 MIN READ
0
Amino acid homeostasis for a Happy New Year!
6 MIN READ
0
Understanding cell type differentiation
3 MIN READ
0
From Hydra to humans vs a Lakatosian research program
4 MIN READ
0
Unified nutritional and molecular mechanisms
9 MIN READ
0
Removing natural selection; reshaping the horse; adjusting evolutionary theory
4 MIN READ
0
Communication, not mutations
2 MIN READ
0
Models by evolutionary biologists are not models
2 MIN READ
0
The future of physics predicts no future for evolutionary theory
3 MIN READ
0
Model organisms: the birds and the bees
3 MIN READ
0
Chemical ecology and RNA-mediated control of DNA loops
< 1 MIN READ
0
Atoms to ecosystems: Evolutionary theory vs the coelacanth
6 MIN READ
0
Jumping back: Science or Pseudoscience? (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Jumping back: Science or Pseudoscience?
6 MIN READ
0
Single-cell level assay of protein biosynthesis and degradation
2 MIN READ
0
Glycine and GnRH: Am I being pedantic?
4 MIN READ
0
Extensive molecular evidence vs ridiculous theories
2 MIN READ
0
Dual genomes: exposing the evolution industry
5 MIN READ
0
One test of bioenergetic health?
2 MIN READ
0
Meaningful dialogue, anonymous fools and idiot minions
4 MIN READ
0
Epigenetic pharmacology and RNA-mediated transciptional landscapes
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated events and "The Theory of Everything"
4 MIN READ
0
Sackler Colloquium: Effects or AFFECTS on Behavior
2 MIN READ
0
Thermodynamic constraints and ecological adaptations sans evolution
6 MIN READ
0
Eliminating correlations from evolutionary ecology
6 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated species specificity
2 MIN READ
0
Are mutations beneficial?
4 MIN READ
0
The key to science: experimental evidence
5 MIN READ
0
Ecological adaptations reported as evolution in insects and mammals
4 MIN READ
0
There’s a model for that!
5 MIN READ
0
Biologists puzzled by evolved RNAs and decaying DNA
6 MIN READ
0
SNPs and millions of small variations in the human genome
3 MIN READ
0
More than a bag of chemicals?
2 MIN READ
0
Achiral GnRH: no prophesy, just prediction
9 MIN READ
0
Nothing new under the sun, except pseudoscientific nonsense
6 MIN READ
0
Making sense of quotes scattered across disciplines
2 MIN READ
0
Intelligent viruses and cancers?
10 MIN READ
0
Complex behaviors of cell types in cancer
6 MIN READ
0
De novo DNA methylation?
3 MIN READ
0
RNA eclipses the importance of DNA to cell type differentiation
4 MIN READ
0
We need pattern recognition, not proclamations
3 MIN READ
0
Pharmacogenomics
3 MIN READ
0
Sexual differentiation of cell types in plants
2 MIN READ
0
A model of MHC 'evolution'
2 MIN READ
0
From deep time into real time: What evolutionary processes?
10 MIN READ
0
In theory, or supported by experimental evidence?
5 MIN READ
0
It’s cell type differention, not cell fate determination (2)
3 MIN READ
0
Are evolutionary theorists 'nob ends'?
5 MIN READ
2
ALPHA GENOMIX
7 MIN READ
2
No excuses: Creation and the meaning of organismal complexity
7 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent gene duplication in plants (but not animals?)
4 MIN READ
0
Evolutionary theorists justify fear of the Ebola viruses
2 MIN READ
0
Evolutionary theorists and evolutionary theists live under rocks
< 1 MIN READ
0
No understanding of biodiversity
2 MIN READ
0
Understanding physical forces of ecological variation and adaptation
< 1 MIN READ
0
Eliminating evolutionary theory
3 MIN READ
0
Behavioral ecology: please continue to believe in our fantasies
3 MIN READ
0
2014 and 2004 Nobel Prize in Medicine
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated events: chromosomal rearrangements and genomic rearrangements
2 MIN READ
2
How much good can be attributed to social science theories?
< 1 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated genetic engineering (Part 3)
< 1 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated genetic engineering (Part 2)
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated genetic engineering
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated events are not a matter of faith
2 MIN READ
0
Color vision refutes the evolutionary dogma of gene duplication
4 MIN READ
0
Unassailable evidence vs assumptions
4 MIN READ
0
Forces of "Nature" limit dissemination of information
4 MIN READ
0
Genomic surveillance ends our world of RNA-mediated ecological adaptations
2 MIN READ
0
Systems biology and memory disorders
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated cell type differentiation and behavior
3 MIN READ
0
Different physical locations and different molecular mechanisms of health and disease
2 MIN READ
0
Metabolism, fixation, health or neurodegerative disorder
2 MIN READ
0
Physics, Chemistry, and Molecular biology (PCMb)
2 MIN READ
0
Physics denied; pseudoscientific nonsense accepted
2 MIN READ
0
Ecological variation and niche construction: 1, 2, 3
6 MIN READ
0
Epigenetically-effected metabolic shifts and ecological adaptations
3 MIN READ
0
Evolving DNA before RNA
4 MIN READ
0
Stop evolutionary theorists. Kill cancers
3 MIN READ
0
Did our adapted mind evolve? (Revisited)
2 MIN READ
0
De novo gene Creation sans evolution of genes via mutations
4 MIN READ
0
Did our adapted mind evolve?
6 MIN READ
0
RNA-directed DNA methylation and RNA-mediated events
5 MIN READ
1
Miracles are not miracles to evolutionary theorists
2 MIN READ
0
Mathematical model: microRNA and epigenetic regulation
2 MIN READ
0
Seemingly futile cycles are not thermodynamically futile
3 MIN READ
0
Do bacterial proteins evolve?
3 MIN READ
0
“Kardashians” in science
< 1 MIN READ
0
Probable changes in connectivity
2 MIN READ
0
New technique used in report of atomic-level ecological adaptations
3 MIN READ
0
Can epigenetic inheritance occur without concurrent changes in morphology AND behavior?
3 MIN READ
0
Memory of repression and memory of behavior (2)
< 1 MIN READ
0
Memory of repression and memory of behavior
2 MIN READ
0
Quantum physics meets Evolutionary Psychology News
2 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent pheromone-controlled exercise-induced physiques
< 1 MIN READ
0
Watching and waiting for more retractions
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated ecological adaptations of teeth
4 MIN READ
0
A molecular visualizer of worthwhile molecular biology
2 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated species diversification from microbes to primates
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated events found everywhere
2 MIN READ
0
Reseachers think copy number variation is genetically determined
< 1 MIN READ
0
Some neuroscientists think a mutation led to human language development
< 1 MIN READ
0
Genotype, observed phenotype, and distinctly disordered behaviors
3 MIN READ
0
Is the problem an internet echo or Feierman's ethics?
2 MIN READ
0
Behavior (3): All responses are RNA-mediated in bees
3 MIN READ
0
RNA-mediated ecological adaptation is not evolution
2 MIN READ
0
Exploding genomes and chromosomal rearrangements via RNA-mediated events
2 MIN READ
0
Behavior (2): All responses are RNA-mediated not genetically-determined
4 MIN READ
0
Behavior: The first response is RNA-mediated not genetically-determined
3 MIN READ
0
Mechanisms that are not understood increase clarity
4 MIN READ
2
Pattern recognition and conserved receptors (TAARs)
5 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent erythropoiesis and anemia
6 MIN READ
0
Evolutionary heritage or ecological adaptation? Racism versus reality
4 MIN READ
0
A relatively young branch of science called epigenetics
4 MIN READ
0
Insect homology and diversity attributed to mutations
2 MIN READ
0
Baby talk: More misrepresentations of ecological adaptations
2 MIN READ
0
A microRNA-mediated mechanism that is epigenetically inherited
2 MIN READ
0
Epimutations: Attacking pseudoscientific dogmas
4 MIN READ
0
Order and disorder: Ecological adaptations not mutations
6 MIN READ
0
microRNAs and species relationships
3 MIN READ
0
Drunks and Monkeys: Pseudoscientific nonsense
2 MIN READ
0
The quantum biology of consciousness
3 MIN READ
0
Behavior is receptor-mediated
10 MIN READ
0
Genes and Race: Human History?
2 MIN READ
0
Soft atheism: a case for Creation
< 1 MIN READ
0
Nutrition, pheromones and cancer (2)
2 MIN READ
0
Ecologically linked adapted ants and brains
2 MIN READ
0
MiRNAs methylation and ecological adaptation sans mutations
2 MIN READ
0
Not focused and self-aggrandizing
2 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent cooperation vs cannibalism (video)
2 MIN READ
0
Another powerful refutation of mutation-initiated natural selection
4 MIN READ
0
The new light of chromosomal rearrangements
3 MIN READ
0
Darwinian theories vs Darwin's facts
2 MIN READ
0
Chromosomal rearrangements and ecological adaptations
4 MIN READ
0
The wrong picture of our evolution
4 MIN READ
0
96 fixed amino acid substitutions, not 96 genes
6 MIN READ
0
Jay R. Feierman
3 MIN READ
0
Don't tell the Creationists
2 MIN READ
0
Targeting a cancer gene
2 MIN READ
0
Alternative splicings (very technical)
2 MIN READ
0
Pulses of olfactory/pheromonal input
2 MIN READ
0
Pheromone-controlled thermodynamics and cancer
2 MIN READ
0
Seeds of life: astrobiological theory and mutations theory
3 MIN READ
0
Your comment is awaiting moderation
2 MIN READ
0
Nutrient-dependent pheromone-controlled stickleback evolution
2 MIN READ
0
Functional coding variants are not mutations
2 MIN READ
0
Mirror neurons and microRNA: theory vs biological facts
4 MIN READ
0
Understanding the role of mutations and evolution
4 MIN READ
0
Evolution: innovations may have non-adaptive origins (sans mutations)
2 MIN READ
0
Are pheromones responsible for human body odour assessment?
2 MIN READ
0
Sex differences in Alzheimer's and everything else
2 MIN READ
0
CB Nemeroff: Off Restriction
< 1 MIN READ
0
A thought experiment
3 MIN READ
0
Honeybees, food odors, and perfume
< 1 MIN READ
0


